Stainless Steels
We supply a full range of stainless steel products, including austenitic stainless steel, ferritic stainless steel, martensitic stainless steel, and duplex stainless steel in the form of plates, coils, bars, and profiles. All products are sourced from leading domestic steel mills.
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Thickness Range | 0.1mm – 30mm (coil); 3.0mm – 50mm (plate) |
| Inner Coil Dia. | 508mm, or slitting and leveling as per customer request |
| Width | 100 – 2000mm |
| Surface Treatment | NO.1, NO.3, NO.4, 2B, 2D, BA, HL, 6K, 8K, Antibacterial, Anti-fingerprint, etc. |
| Standards | GB, ASTM, EN, JIS etc. |
Introduction
Stainless steel is an alloy steel with excellent corrosion resistance, primarily composed of iron, chromium, and small amounts of other alloying elements such as nickel, molybdenum, titanium, and aluminum. It offers outstanding oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, and good mechanical and processing properties, making it widely used in various industries. Stainless steel can be classified and manufactured according to different alloy compositions and performance requirements.
What is Stainless Steels
Stainless steel is an alloy material based on iron, containing at least 10.5% chromium and other elements such as nickel, molybdenum, titanium, and copper. Chromium forms a dense chromium oxide film on the surface of the steel, which effectively prevents oxidation and corrosion under normal temperatures and various chemical environments. Different alloy compositions and manufacturing processes result in varying properties and application fields of stainless steel.
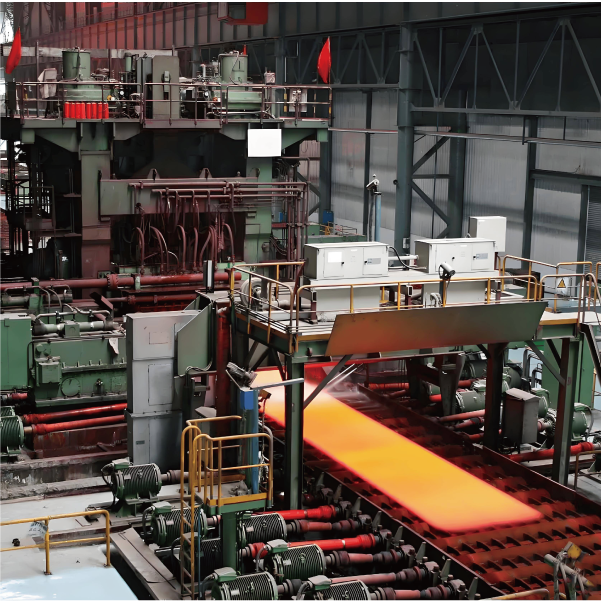
Production Process of Stainless Steels
The production of stainless steel mainly involves the following steps:
- Smelting and Alloying
- Raw materials such as iron ore, scrap steel, and alloying elements (chromium, nickel, molybdenum, etc.) are melted in an electric furnace at high temperatures. The smelting process requires precise control of temperature, alloy composition, and impurities to ensure the quality of the stainless steel.
- Casting and Forming
- After smelting, the molten steel is cast into ingots, plates, bars, and pipes through casting and continuous casting processes for further processing.
- Heat Treatment
- Heat treatment enhances the mechanical properties, grain structure, and corrosion resistance of stainless steel. Common methods include annealing, solution treatment, and aging treatment. Heating and slow cooling eliminate internal stress and improve hardness and ductility.
- Cold Working and Surface Treatment
- After heat treatment, stainless steel typically undergoes cold working processes such as rolling, drawing, and extrusion to achieve the desired size and surface quality. Surface treatments like polishing, sandblasting, and electro-polishing improve both appearance and corrosion resistance.
- Inspection and Quality Control
- Each stage of production involves strict control over chemical composition, mechanical properties, and surface quality. Testing includes chemical analysis, tensile strength, hardness, elongation tests, and surface defect inspection to ensure product quality meets the required standards.
Classification of Stainless Steels
Stainless steel can be classified into the following main types based on structure, composition, and performance:
- Austenitic Stainless Steel – Austenitic stainless steel is the most commonly used type, characterized by high chromium and nickel content, excellent corrosion resistance, and good formability and weldability.
- 304 Stainless Steel – Widely used in kitchenware, chemical equipment, and medical instruments.
- 316 Stainless Steel – Contains molybdenum for enhanced corrosion resistance, ideal for marine and chemical applications.
- Ferritic Stainless Steel – Ferritic stainless steel primarily consists of iron and chromium, without nickel. It offers good corrosion and heat resistance at a lower cost but has lower ductility compared to austenitic stainless steel.
- Common grades: 430, 444
- Martensitic Stainless Steel – Martensitic stainless steel contains higher carbon content, providing high strength and hardness but lower corrosion resistance. It’s commonly used in applications requiring strength and wear resistance.
- Common grades: 410, 420
- Duplex Stainless Steel – Duplex stainless steel combines austenitic and ferritic structures, offering superior corrosion resistance, strength, and ductility. It is mainly used in oil, gas, and chemical industries.
- Common grades: 2205, 2507
- Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steel – Precipitation-hardening stainless steel achieves high strength through aging treatment and has good corrosion resistance.
- Common grades: 17-4PH, 15-5PH
- Used in aerospace and chemical industries.
Standards for Stainless Steels
Stainless steel production and application follow international and national standards:
| Category | Features | Grades (China/GB) | Grades (USA/ASTM/UNS) | Grades (Europe/EN) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | Strong corrosion resistance, good plasticity, high toughness, suitable for forming processes. | 304, 316, 321, 304L, 316L | 304 (S30400), 316 (S31600), 321 (S32100), 304L (S30403), 316L (S31603) | 1.4301, 1.4404, 1.4541 | Chemical equipment, food processing equipment, architectural decorations, pharmaceutical equipment, etc. |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | High chromium content, good corrosion resistance, low cost, average welding performance. | 430, 409, 439 | 430 (S43000), 409 (S40900), 439 (S43035) | 1.4016, 1.4512, 1.4509 | Automotive exhaust systems, home appliances, construction decoration, chemical equipment, etc. |
| Martensitic Stainless Steel | High strength, high hardness, moderate corrosion resistance. | 410, 420, 440C | 410 (S41000), 420 (S42000), 440C (S44004) | 1.4006, 1.4021, 1.4125 | Knives, valves, bearings, medical instruments, etc. |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | Combines features of austenitic and ferritic grades, offering high strength and corrosion resistance. | 2205 (S31803/S32205), 2507 | S31803, S32205, S32750 | 1.4462, 1.4410 | Oil and gas pipelines, chemical storage tanks, marine engineering equipment, etc. |
| Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel | Achieves high strength and good corrosion resistance through heat treatment. | 17-4PH (0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb), 15-5PH | 17-4PH (S17400), 15-5PH (S15500) | 1.4542 | Aerospace, nuclear industry, chemical equipment, and other high-performance applications. |
| Super Austenitic Stainless Steel | Exceptional corrosion resistance for specialized environments. | 254SMO | UNS S31254 | 1.4547 | Seawater desalination, chemical industries. |
| High Chromium Heat-Resistant Stainless Steel | Heat resistant, suitable for high-temperature environments. | 310S | UNS S31008 | 1.4845 | High-temperature industrial equipment, boiler components. |
Standards:
ASTM A240, A268, A276, A297, A312, A693, A789; GB/T 1220, GB/T 3280, GB/T 4237, GB/T 21833; EN 10088-1, 2, 3, 4.
Application for Stainless Steels
Stainless steel’s superior corrosion resistance, strength, and high-temperature performance make it widely used across industries:
- Construction and Architectural Decoration – Due to its elegant appearance and corrosion resistance, stainless steel is widely used in building facades, roofing, railings, and window frames.
- Common grades: 304, 316
- Food and Pharmaceutical Industry – Stainless steel is non-toxic, easy to clean, and corrosion-resistant, making it ideal for food processing equipment, pipelines, tanks, and containers.
- Chemical and Petrochemical Industry – Stainless steel is widely used in pressure vessels, reactors, pipelines, and heat exchangers, particularly in corrosive environments.
- Common grade: 316
- Medical Instruments – Stainless steel is biocompatible and widely used for surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices.
- Automotive and Transportation – Stainless steel is used in structural components, exhaust systems, and wheels in the automotive and transportation industries.
- Common grades: 304, 430
- Energy and Environmental Protection – Stainless steel is used in nuclear, solar, and wind energy equipment, as well as in environmental protection systems such as wastewater treatment and exhaust gas purification.
- Home Appliances – Stainless steel enhances the durability and corrosion resistance of home appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, and microwave ovens.
Summary
Stainless steel is a key material known for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and high-temperature resistance. Its versatility makes it widely applicable in construction, food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, energy, transportation, and home appliances. The diverse alloy compositions and performance characteristics of stainless steel allow it to meet the requirements of various industries.
Warehouses






Workability
HK Hantie’s laminated metal products are versatile in processing, offering capabilities such as deep drawing, steel sheet punching, V-bending, 180° bending, printing, CNC engraving, and custom requests.
We also provide cutting services for film-coated glass to meet customer needs.






Packing & Delivery
Export packaging or customized packaging as per customer requirements, with reinforced protection during shipment to ensure product stability.






FAQ
Relative Products
Steel Plates Medium and heavy plates refer to steel plates with a thickness generally ranging from 4mm to 100mm. They are
Stainless Steels We supply a full range of stainless steel products, including austenitic stainless steel, ferritic stainless steel, martensitic stainless steel,
Cold Rolled Steel Coils Cold Rolled Steel Coils Full Range of Cold-Rolled Steel ProductsWe supply a full range of cold-rolled steel
Contact