
Clad Plates
Clad Plates
Our Clad Metal Plates are composite metal materials formed by metallurgically bonding one or more layers of precious metal corrosion-resistant alloys with a more cost-effective high-strength substrate through explosive cladding or roll bonding processes. The clad materials typically include titanium, zirconium, tantalum, silver, copper, aluminum, nickel-based alloys, stainless steel, and others, while the substrates are generally high-strength carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and similar materials.
As a new, high-performance, and cost-effective material, clad metal plates combine the characteristics of both the base and clad materials. They typically exhibit a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent high-temperature resistance, and superior corrosion resistance. The performance of these plates depends not only on the properties of the base and clad materials but also on their composition and distribution. Compared to single homogeneous materials, clad plates offer superior overall performance, better workability, and a wider range of metal combinations, significantly reducing material procurement costs for customers.
Clad metal plates feature a high bonding strength between the clad material and the substrate, with a bonding rate close to 100%. They also have excellent welding and processing performance, while costing only 30% to 50% of pure single-material alternatives. These plates are primarily used in process equipment and pressure vessels in the chemical industry, methanol fuel tanks in shipbuilding, as well as in the power, marine engineering, paper, environmental protection, and light industries.
Depending on the manufacturing method, our company can produce both explosive clad plates and roll-bonded clad plates.


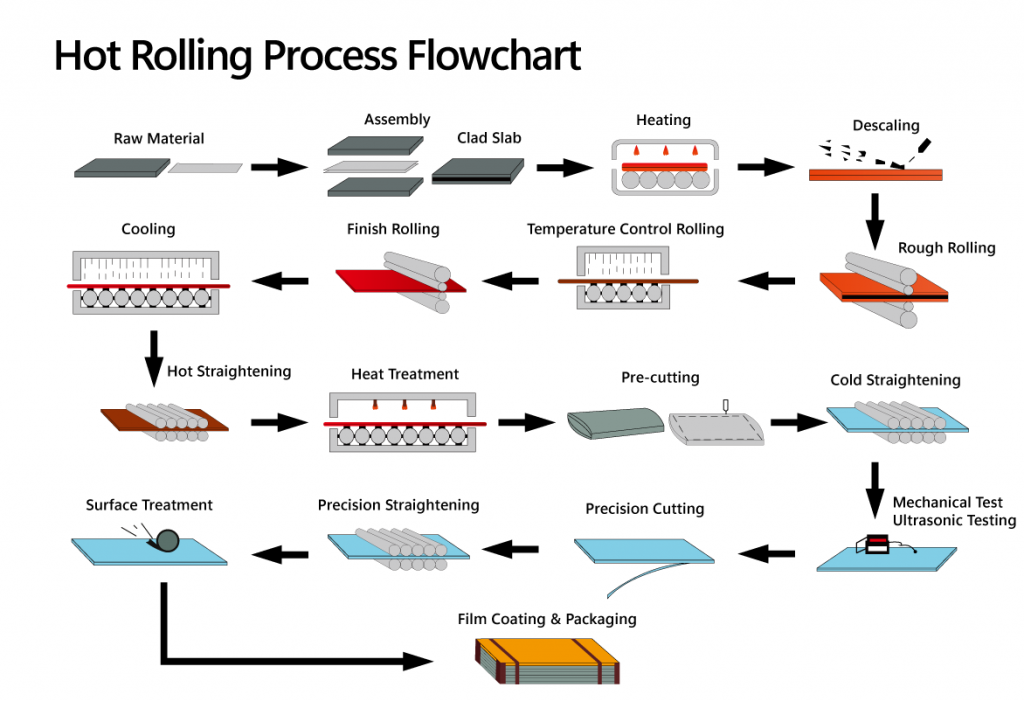
Roll Bonding Process
Roll Bonding Process is a technique where a substrate is bonded with one or more thinner cladding materials (in a “hamburger” configuration) through high-temperature, high-pressure rolling, resulting in a uniform and strong metallurgical bond between the metals. The process offers the following advantages:
Below is roll bonding production process:
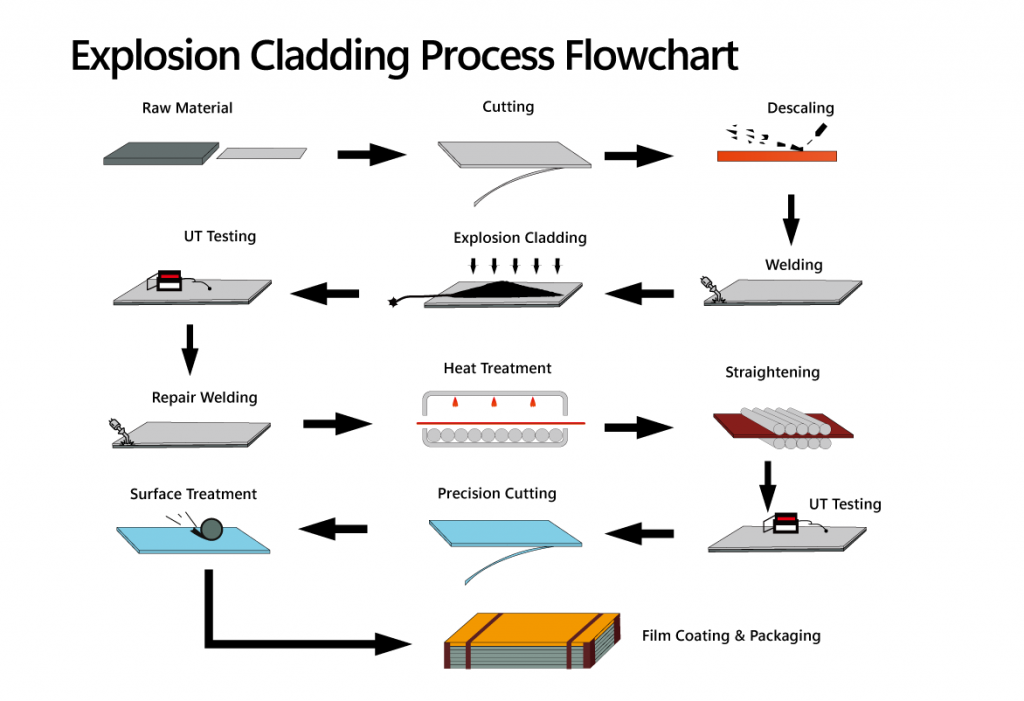
Explosive Bonding Process
Explosive Bonding Process uses explosives as an energy source to cause a high-speed oblique collision between the metal surfaces being bonded. This process creates a thin transition layer on the surface with characteristics of plastic deformation, melting, diffusion, and wave-like patterns, resulting in a strong metallurgical bond between the metals. The Explosive Roll Bonding Process involves initially welding the materials through explosive bonding, followed by hot rolling, cold rolling, or a combination of hot and cold rolling. This method offers the following advantages:
Below is the explosive bonding production process:
Equipments
Producing Equipments




Testing Equipments




Order Conditions
Our Advantages
Standards and Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance
Production according to
Stainless steel clad plates: ASME SA263, SA264, ASTM A263, A264, (BS) EN 10088-2, and additional specific requirements.
Nickel & nickel alloy clad plates: ASME SA265, ASTM A265.
Titanium, niobium, zirconium, tantalum, aluminum and the alloy clad plates: ASME SB898, ASTM B898.
Copper & the alloy clad plates: ASTM B432.
Others: API 5L, DNV (OF 101) and other classification societies.
Testing items: impact test, through-thickness test by ASTM A770 S3, UT by ASTM A-578 Level A, S1, PWHT by ASME Section VIII Division 1, UCS-56, HIC by NACE MR0175, HIC testing report by NACE TM0284 for instance.
Base Metal Grades
Structural and pressure vessel steels:
| Standard | Grade |
|---|---|
| ASME SA516(M), ASTM A516(M) | 55, 60, 65, 70 |
| ASME SA572(M), ASTM A572(M) | 42, 50, 55, 60, 65. type: 1, 2, 3, 5 |
| ASME SA285(M), ASTM A285(M) | A, B, C |
| ASME SA204(M), ASTM A204(M) | A, B, C |
| ASME SA302(M), ASTM A302(M) | A, B, C, D |
| ASME SA533(M), ASTM A533(M) | Type A, B, C, D, E. Class 1, 2, 3. |
| ASME SA387(M), ASTM A387(M) | 5, 9, 11, 12, 22, 91. Class 1, 2. |
| ASME SA542(M), ASTM A542(M) | Type A, B, C, D, E. Class 1, 2, 3, 4, 4a. |
| ASME SA841(M), ASTM A841(M) | A, B, C, D, E, F. Class 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8. |
| Standard | Grade |
|---|---|
| ASME SA106(M), ASTM A106(M) | A, B, C |
| ASME SA672(M), ASTM A672(M) | A50, C60, C65, C70, H80, J80, J90, L65, L70, L75 |
| ASME SA860(M), ASTM A860(M) | WPHY 42, WPHY 46, WPHY 52, WPHY 60, WPHY 65, WPHY 70 |
| API 5L | B, X52, X60, X65, level PSL2 |
| DNV OS-F101 | SAWL 245, SAWL 360, SAWL 415, SAWL 450 |
Ship-building steels: ASTM A36/A36M, ASME SA36/SA36M
Bridge steels: ASME SA709/SA709M, ASTM A709/A709M, grade 36, 50, 50S, 50W, HPS 50W, HPS 70W, 100, 100W
Clad Layer Grades
| Standard | Grade |
|---|---|
| ASME SA240, ASTM A240 | 410, 410S, 304, 304L, 321, 347, 316L, 316Ti, 317L, 317LMN, 904L |
Special steels, non-ferrous metals and alloys:
| Standard | Grade |
|---|---|
| ASTM B409, ASME SB409 | Alloy 800 UNS N08800 |
| ASTM B709, ASME SB709 | Alloy 28 UNS N08028 |
| ASTM B677, ASME SB677 | Alloy 925 UNS N08925, alloy 926 UNS N08926 |
| ASTM B463, ASME SB463 | Alloy 20 UNS N08020 |
| ASTM B424, ASME SB424 | Alloy 825 UNS N08825 |
| ASTM B443, ASME SB443 | Alloy 625 UNS N06625 |
| ASTM B575, ASME SB575 | Alloy C22 UNS N06022, alloy C4 N06455, alloy C276 N10276, alloy 59 N06059 |
| ASTM B333, ASME SB333 | Alloy B2 UNS N10665 |
| ASTM B168, ASME SB168 | Alloy 600 UNS N06600, alloy 601 UNS N06601 |
| ASTM B127, ASME SB127 | Alloy 400 UNS N04400 |
| ASTM B162, ASME SB162 | Alloy 200 UNS N02200, alloy 201 UNS N02201 |
| ASTM B152, ASME SB152 | Alloy C122 UNS C12200 |
| ASTM B171, ASME SB171 | Alloy CuNi 90/10 UNS C70600, alloy CuNi 70/30 UNS C71500 |
| Standard | Grade |
|---|---|
| ASTM B265, ASME SB265 | Grade 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 12, 23 |
| ASTM B348, ASME SB348 | Grade 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 12, 23 |
| ASTM F67, ASME SF67 | Grade 4 |
| ASTM B381, ASME SB381 | F2, F5, F12 |
| ASTM F136, ASME SF136 | Ti6Al4V |
Others: AMS 4901T, AMS 4911N, AMS 4905, AMS 4911, AMS 4919, AMS 4928, AMS-T-9046, DMS1592, BS TA10, BS TA56
We can do much more for our customers!


CERTIFICATION
The company has achieved ISO 9001 Quality Management System certification, ISO 14001 Environmental Management System certification, and Occupational Health and Safety Management System certification. Other certifications, such as PED and API, are currently in the application process. Our clad plate products have also received CE certification for pressure vessels, while our marine clad plates have been certified by six national classification societies, including CCS, DNV GL, LR, BV, RINA, and ABS.







DELIVERY AND PACKING
Below is our standard packing method for export transportation, for other special requirements from our customers, we can customize. The surface of the clad plates is covered with a PE plastic film, followed by a layer of hard cardboard for protection. The outermost layer is waterproofed, and labels are applied to ensure effective identification. The product is then loaded for shipment.






Contact


